GoTTY - Share your terminal as a web application
GoTTY is a simple command line tool that turns your CLI tools into web applications.
Installation
Download the latest binary file from the Releases page.
Homebrew Installation
You can install gotty with Homebrew as well.
$ brew tap yudai/gotty
$ brew install gotty
go get Installation
If you have a Go language environment, you can install gotty with the go get command.
$ go get github.com/yudai/gottyUsage
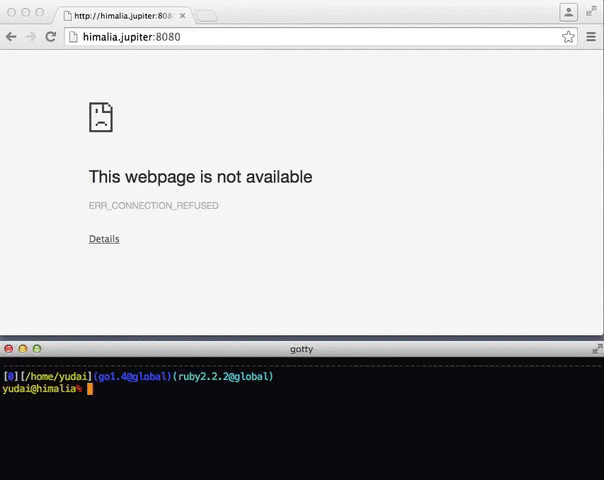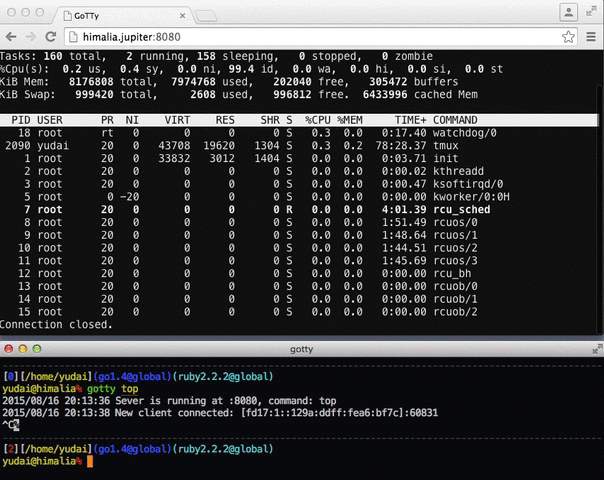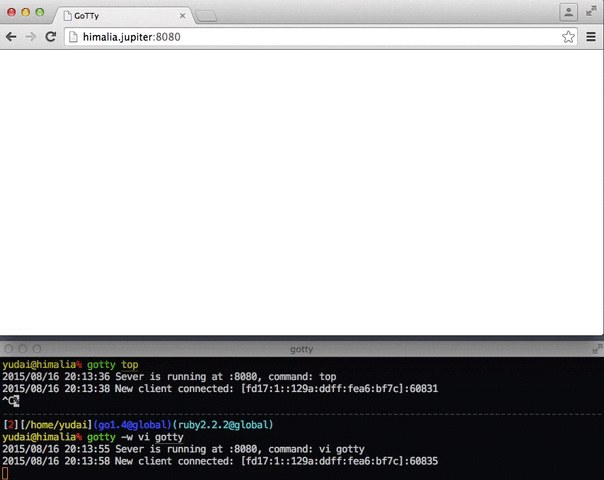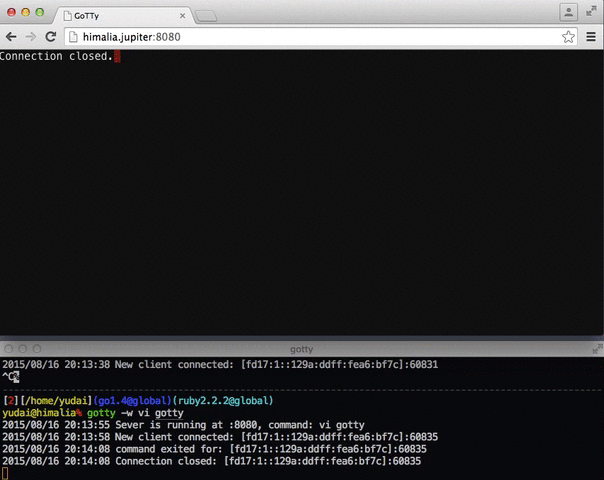
Usage: gotty [options] <command> [<arguments...>]Run gotty with your preferred command as its arguments (e.g. gotty top).
By default, gotty starts a web server at port 8080. Open the URL on your web browser and you can see the running command as if it's running on your terminal.
Options
--addr, -a IP address to listen [$GOTTY_ADDR]
--port, -p "8080" Port number to listen [$GOTTY_PORT]
--permit-write, -w Permit clients to write to the TTY (BE CAREFUL) [$GOTTY_PERMIT_WRITE]
--credential, -c Credential for Basic Authentication (ex: user:pass) [$GOTTY_CREDENTIAL]
--random-url, -r Add a random string to the URL [$GOTTY_RANDOM_URL]
--profile-file, -f "~/.gotty" Path to profile file [$GOTTY_PROFILE_FILE]
--title-format "GoTTY - {{ .Command }} ({{ .Hostname }})" Title format of browser window [$GOTTY_TITLE_FORMAT]
--version, -v print the versionBy default, gotty doesn't allow clients to send any keystrokes or commands except terminal window resizing. When you want to permit clients to write input to the PTY, add the -w option. However, accepting input from remote clients is dangerous for most commands. Make sure that only trusted clients can connect to your gotty server when you activate this option. If you need interaction with the PTY, consider starting gotty with tmux or GNU Screen and run your main command on it.
Profile File
You can customize your terminal (hterm) by providing a profile file to the gotty command, which is a JSON file that has a map of preference keys and values. Gotty loads a profile file at ~/.gotty by default when it exists.
The following example makes the font size smaller and the background color a little bit blue.
{
"font-size": 5,
"background-color": "rgb(16, 16, 32)"
}Available preferences are listed in the hterm source code
Sharing with Multiple Clients
Gotty starts a new process when a new client connects to the server. This means users cannot share a single terminal with others by default. However, you can use terminal multiplexers for sharing a single process with multiple clients.
For example, you can start a new tmux session named gotty with top command by the command below.
$ gotty tmux new -A -s gotty topThis command doesn't allow clients to send keystrokes, however, you can attach the session from your local terminal and run operations like switching the mode of the top command. To connect to the tmux session from your terminal, you can use following command.
$ tmux new -A -s gottyBy using terminal multiplexers, you can have the control of your terminal and allow clients to just see your screen.
Quick Sharing on tmux
To share your current session with others by a shortcut key, you can add a line like below to your .tmux.conf.
# Start gotty in a new window with C-t
bind-key C-t new-window "gotty tmux attach -t `tmux display -p '#S'`"Playing with Docker
When you want to create a jailed environment for each client, you can use Docker containers like following:
$ gotty -w docker run -it --rm busyboxDevelopment
You can build a binary yourself using following commands. Windows is not supported now.
# Install tools
go get github.com/jteeuwen/go-bindata/...
go get github.com/tools/godep
# Checkout hterm
git submodule sync && git submodule update --init --recursive
# Restore libraries in Godeps
godep restore
# Build
makeArchitecture
Gotty uses hterm to run a JavaScript based terminal on web browsers. Gotty itself provides a websocket server that simply relays output from the PTY to clients and receives input from clients and forwards to the PTY. This hterm + websocket idea is highly inspired by Wetty.
License
The MIT License